
Both Ras (a GTPase) and Src (protein tyrosine kinase) are known to be modified in this manner.

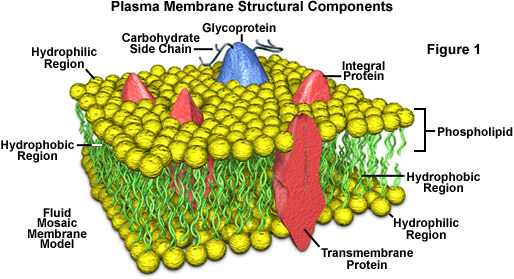
One method involves irreversible covalent modification. Proteins can be attached to the cell membrane in a variety of ways. Membrane proteins can be attached to both the outside and inside of the cell membrane.
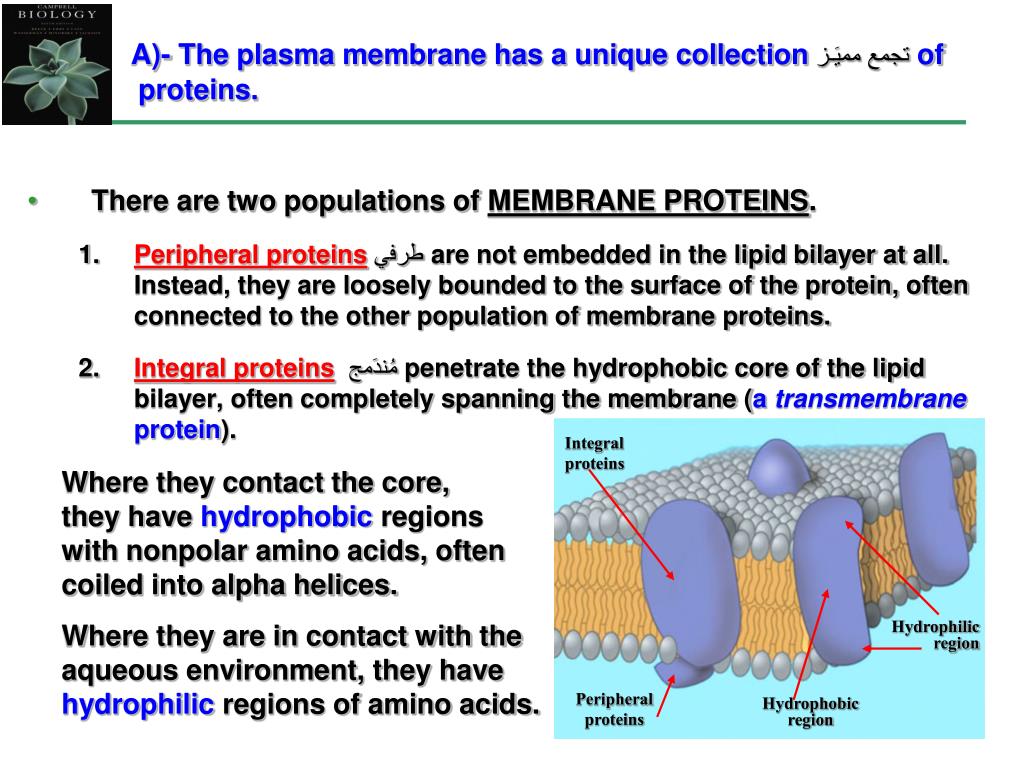
Others are embedded within the lipid bilayer of a cell often form channels and pores. Some membrane proteins are found bounded to lipid bilayer and generally involved in cell-cell signaling or interactions. Membrane proteins can be classified into two groups based on the strength of their association with the membrane: Membrane proteins can be attached to the membrane or associated with the membrane of a cell or an organelle. They may span across the entire phospholipid bi-layer, or be monotopic.īiological membranes have phospholipid bilayer structure which contains a set of proteins which help plasma membrane to carry its distinctive functions. Essentially, they are permanently bounded to the membrane. Integral proteins: (also called intrinsic proteins) These are proteins are characterized by strong interaction with the membrane, which can only be broken by the addition of detergents or some other nonpolar solvent.The two main categories are listed below: Theses proteins fall into two main categories, depending upon how strongly the protein interacts with the membrane. They may also act as channels that move specific molecules into and out of the membrane. Due to their many functions in the membrane, they are in high concentration on the surface of the membrane. The membrane proteins also play a strong role in controlling a wide array of gradients such as chemical, electrical, and mechanical gradients and are responsible for cell structure during key cell events such as division. They participate in various biological processes, such as cell signaling-transduction pathways. The same forces cause hydrophobic amino acids to pack in the interior of proteins, away from the aqueous environment.A membrane protein is any protein found in a biological membrane. Hydrophobic amino acids have aliphatic side chains, which are insoluble or only slightly soluble in water. Why are hydrophobic amino acids located in the interior? Some amino acids have polar ( hydrophilic) side chains while others have non-polar ( hydrophobic) side chains. The cell is an aqueous (water-filled) environment. Proteins, made up of amino acids, are used for many different purposes in the cell. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane.Ĭonsidering this, are proteins hydrophobic or hydrophilic? The portions of an integral membrane protein found inside the membrane are hydrophobic, while those that are exposed to the cytoplasm or extracellular fluid tend to be hydrophilic.įurthermore, what makes a protein hydrophobic? Hydrophobic amino acids are those with side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous (i.e. Regarding this, is the inside of a cell hydrophobic or hydrophilic? Proteins must therefore be hydrophilic (" water loving") in order to be suspended in this environment. Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic The interior and the exterior of cells is liquid, usually a solution or suspension of ions, small molecules and large molecules dissolved in water.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
